R134a Refrigerant Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Accessing R134a pressure-temperature charts in PDF format online is crucial for technicians. Numerous sources offer these charts, vital for diagnosing AC systems and understanding refrigerant behavior.

Understanding R134a Refrigerant
R134a, a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC), emerged as a prominent replacement for R-12, a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) damaging to the ozone layer. Its widespread adoption stems from its zero ozone depletion potential (ODP), making it an environmentally preferable alternative in numerous applications. Commonly utilized in automotive air conditioning, residential refrigerators, and various commercial refrigeration systems, R134a offers a balance of thermodynamic properties suitable for medium-temperature cooling.
However, it’s crucial to recognize that R134a possesses a significant global warming potential (GWP), prompting ongoing research and development of newer, more sustainable refrigerants. Understanding its properties – including its chemical formula (CH2FCF3) and phase behavior – is fundamental for effective system operation and maintenance. Technicians rely heavily on R134a pressure-temperature charts, readily available online in PDF format, to accurately assess system performance and diagnose potential issues. These charts correlate pressure and temperature, providing critical data for determining refrigerant charge, identifying leaks, and evaluating component functionality. Proper handling and adherence to safety precautions are paramount when working with R134a.
R134a Properties and Applications
R134a exhibits key properties including a boiling point of -26.3°C (-15.3°F) at atmospheric pressure and a relatively low toxicity. It’s a non-flammable refrigerant, enhancing safety during handling and operation. Its thermodynamic characteristics make it efficient in vapor-compression refrigeration cycles, though less efficient than newer alternatives like R410a in terms of cooling capacity per unit mass.
The applications of R134a are diverse. It’s extensively used in automotive air conditioning systems, providing cabin cooling. Residential refrigerators and freezers commonly employ R134a for maintaining low temperatures. Commercial refrigeration, including supermarket display cases and vending machines, also relies on this refrigerant. Furthermore, it finds use in chillers for building air conditioning and industrial processes.
Despite its benefits, the high GWP of R134a is driving a transition towards lower-GWP alternatives. Accessing R134a pressure-temperature charts (often found online as PDFs) remains vital for servicing existing systems, enabling technicians to accurately diagnose and repair equipment utilizing this widely-deployed refrigerant.

The Importance of Pressure-Temperature Charts
Pressure-temperature (P-T) charts are indispensable tools for HVAC/R technicians. They graphically represent the relationship between a refrigerant’s pressure and its corresponding saturation temperature – the temperature at which it changes phase (liquid to gas or vice versa). This correlation is fundamental to understanding system performance and diagnosing issues.
Without a P-T chart, accurately assessing refrigerant charge, identifying restrictions, or determining system efficiency becomes significantly more difficult. Technicians use these charts to verify if a system is operating within normal parameters. Deviations from expected pressure-temperature readings indicate potential problems like overcharging, undercharging, or component failures.
R134a charts, readily available online as PDFs, are specifically calibrated for this refrigerant. They allow for precise determination of system conditions. Manufacturers distribute these charts extensively, recognizing their critical role in proper system maintenance. Accessing a reliable R134a chart is the first step in effective troubleshooting and repair, ensuring optimal system operation and longevity.

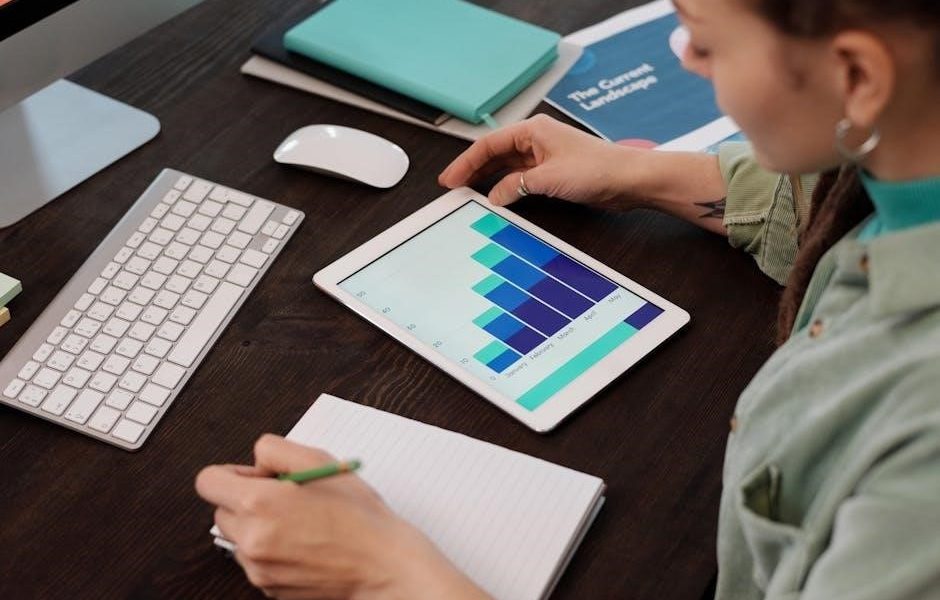
Reading an R134a Pressure-Temperature Chart
Interpreting an R134a pressure-temperature chart requires understanding its axes. The pressure scale, typically in PSIG, is displayed horizontally, while the temperature scale, usually in Fahrenheit or Celsius, runs vertically. Finding the intersection of a measured pressure and corresponding saturation temperature reveals the refrigerant’s state.
Locating a specific pressure on the chart, then drawing a horizontal line to intersect with the temperature scale, provides the saturation temperature at that pressure. Conversely, knowing the temperature allows you to find the corresponding saturation pressure. Remember that these charts represent saturation conditions – where liquid and vapor coexist.
Understanding the chart’s data points – including saturation lines, critical points, and specific volume/entropy information – enhances diagnostic capabilities. Online R134a charts (PDF format) often include additional data for comprehensive analysis. Accurate readings and chart interpretation are vital for effective system diagnosis and repair, ensuring optimal performance.
Chart Components: Saturation Pressure and Temperature
Central to an R134a chart are saturation pressure and temperature, representing the conditions where liquid and vapor phases coexist in equilibrium. Saturation pressure indicates the refrigerant’s boiling point at a given temperature. As pressure increases, so does the saturation temperature – and vice versa.
The saturation pressure line on the chart visually depicts this relationship. Points along this line represent the boiling or condensing points of R134a at various pressures. Understanding this line is crucial for diagnosing system issues, such as low refrigerant charge or restrictions.

Online R134a charts (PDF format) clearly illustrate these components. They often include data tables alongside the graphical representation, providing precise values for pressure and temperature. Accurate interpretation of these values is essential for determining system performance and identifying potential problems. Mastering these concepts allows for effective troubleshooting and repair.
Subcooling and Superheat Explained
Subcooling and superheat are critical concepts when analyzing R134a systems, and readily visualized using comprehensive charts available online in PDF format. Subcooling refers to cooling the liquid refrigerant below its saturation temperature at a given pressure, ensuring it remains a liquid before entering the metering device.
Superheat, conversely, describes heating the refrigerant vapor above its saturation temperature after it exits the evaporator. This ensures only vapor enters the compressor, preventing damage. Both values are essential for optimal system performance.
R134a charts help determine appropriate subcooling and superheat levels. Technicians use pressure-temperature readings and the chart to calculate these values. Proper subcooling prevents flash gas, while correct superheat avoids liquid slugging. Online resources provide detailed explanations and examples, aiding in accurate diagnosis and efficient system operation. Mastering these concepts is vital for effective HVAC/R service.
Using the Chart for System Diagnosis
R134a pressure-temperature charts, easily accessible online as PDFs, are indispensable diagnostic tools for HVAC/R technicians. By comparing measured system pressures and temperatures to the chart, professionals can quickly identify potential issues. For example, abnormally low pressure suggests a refrigerant leak or restricted flow.
High pressure could indicate a condenser blockage or overcharge. Deviations from expected subcooling and superheat values, determined using the chart, pinpoint specific component failures. A chart helps verify proper refrigerant charge and assess evaporator and condenser performance.
Accurate diagnosis relies on precise pressure and temperature readings combined with chart interpretation. Online resources often provide troubleshooting guides alongside the charts, enhancing diagnostic capabilities. Utilizing these tools minimizes guesswork, leading to faster repairs and improved system efficiency. Proper chart usage is fundamental to effective HVAC/R service and maintenance.
R134a Chart Data Interpretation: Example Scenarios
Scenario 1: Low Suction Pressure. A system displays 20 PSI on the suction side at an ambient temperature of 80°F. Consulting an R134a chart (available online as a PDF) reveals this indicates a refrigerant undercharge or a restriction in the refrigerant line, potentially at the evaporator.
Scenario 2: High Head Pressure. A reading of 250 PSI on the high side, with a 90°F condensing temperature, suggests a condenser issue – possibly blockage or airflow restriction. The chart confirms this pressure is significantly elevated for those conditions.
Scenario 3: Incorrect Superheat. Measuring 10°F superheat when the chart indicates 15-20°F suggests a metering device malfunction, potentially a TXV stuck open. Accurate interpretation, using readily available online charts, is crucial for pinpointing the root cause and implementing effective repairs. These examples demonstrate how charts translate readings into actionable diagnostic insights.
R134a vs. Other Refrigerants (R410a Comparison)
R410a boasts a significantly higher cooling capacity per unit mass – more than double that of R134a. This translates to smaller compressor sizes for equivalent cooling output. However, R410a’s energy efficiency is approximately 10% lower than R134a. Crucially, R410a operates at substantially higher pressures; reaching up to 4MPa, compared to R134a’s maximum of around 2MPa.
System Implications: R410a systems demand higher pressure-rated components and more robust materials. While R134a is widely used in older automotive AC systems and some refrigeration applications, R410a has become the standard in residential and light commercial air conditioning. Understanding these differences, often detailed in comparative charts available online as PDFs, is vital for correct servicing and refrigerant selection.
Environmental Note: Both are HFCs, but R410a has a higher Global Warming Potential (GWP) than R134a, driving the industry towards newer, lower-GWP alternatives.
Impact of Saturation Temperature on Condenser Performance
The saturation temperature of R134a directly influences condenser performance. A higher saturation temperature – resulting from increased evaporator load – demands a higher condensing temperature to maintain efficient heat rejection. This, in turn, increases the pressure difference across the condenser, impacting fan speed and energy consumption.

Heat Transfer: Lower saturation temperatures reduce the temperature difference between the refrigerant and the ambient air, diminishing the driving force for heat transfer within the condenser. Numerical simulations, as explored in research, demonstrate this relationship. Accurate R134a charts, readily available online in PDF format, are essential for predicting these effects.
Condenser Design: Understanding this impact is critical for condenser design and optimization. Factors like fin spacing, tube diameter, and airflow are adjusted to compensate for varying saturation temperatures, ensuring optimal heat rejection and system efficiency. Proper diagnosis, aided by pressure-temperature charts, allows technicians to identify condenser issues related to saturation temperature.
Multiphase Flow and R134a Condensation
R134a condensation within HVAC and refrigeration systems invariably involves multiphase flow – a complex interaction of liquid and vapor phases. As R134a transitions from a superheated vapor to a saturated liquid within the condenser, understanding this flow regime is crucial for optimizing heat transfer and system efficiency.
Condensation Process: The process isn’t simply a phase change; it’s accompanied by significant changes in density and flow patterns. Numerical simulations, as highlighted in recent studies, are used to analyze this phenomenon, revealing the impact of factors like tube geometry and refrigerant velocity. Access to accurate R134a charts, often found online as PDFs, aids in interpreting these simulations.
Flow Regimes: Different flow regimes – stratified, annular, and slug flow – occur during condensation, each with unique heat transfer characteristics. Proper system design and control strategies must account for these variations. Diagnosing issues related to multiphase flow requires a thorough understanding of R134a’s properties, readily available through reliable pressure-temperature charts.

Refrigerant Designation and ASHRAE Standards
Refrigerant nomenclature, like that of R134a, originated with the need to standardize identification of fluorocarbon refrigerants. Early designations were linked to chemical composition, as defined by ASHRAE Standard 34-67. This system connects the refrigerant’s code to its chemical formula, allowing for precise identification.
ASHRAE’s Role: The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) plays a pivotal role in establishing and updating refrigerant standards. These standards cover safety classifications, physical properties, and testing procedures. Understanding these standards is vital for technicians working with R134a.
R134a’s Designation: The “R” denotes a refrigerant, followed by a numerical code indicating its composition. R134a (HFC-134a) is a hydrofluorocarbon, meaning it contains hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon. Accessing reliable data, such as that found in R134a charts available online in PDF format, ensures adherence to ASHRAE guidelines and safe handling practices. Proper designation and adherence to standards are crucial for system performance and environmental responsibility.
Environmental Considerations of R134a
While R134a doesn’t deplete the ozone layer – a significant improvement over earlier CFC refrigerants – it’s a potent greenhouse gas. Its Global Warming Potential (GWP) is considerably higher than that of carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change. This has driven the search for, and adoption of, lower-GWP alternatives.
Regulatory Pressure: Due to its environmental impact, R134a is facing increasing regulatory scrutiny globally. Various regions are implementing phase-down strategies, encouraging or mandating the use of more environmentally friendly refrigerants. Understanding these regulations is crucial for compliance.
Responsible Handling: Proper handling and leak prevention are paramount when working with R134a. Minimizing refrigerant emissions is essential to reduce its environmental footprint. Utilizing resources like R134a charts (available online in PDF format) aids in accurate system diagnosis and efficient servicing, reducing the likelihood of leaks. The transition to alternative refrigerants is ongoing, driven by the need for sustainable cooling solutions.
R134a Applications: Common Uses
R134a has historically been widely utilized across numerous cooling applications, primarily as a replacement for R-12. Common applications include automotive air conditioning systems, where it became the standard refrigerant for many years. It’s also found in medium-temperature refrigeration, such as commercial refrigerators and display cases in supermarkets.
Beyond Automotive: R134a’s applications extend to residential refrigerators, freezers, and dehumidifiers. It’s also employed in chillers for commercial and industrial cooling, and in some specialized applications like vending machines and drinking water coolers. Accessing resources like R134a charts (often available online as PDFs) is vital for servicing these diverse systems.
Transitioning Landscape: While still present in many existing systems, R134a is gradually being phased out in favor of lower-GWP alternatives. However, understanding its properties and applications remains crucial for technicians maintaining and repairing older equipment. Proper diagnosis, aided by accurate charts, ensures efficient and responsible servicing.
Locating R134a Charts Online (PDF Format)
Finding reliable R134a pressure-temperature charts in PDF format is readily achievable through various online resources. Many HVAC/R industry websites and refrigerant suppliers offer downloadable charts for free. A simple web search using terms like “R134a chart PDF” or “R134a pressure temperature chart” yields numerous results.
Manufacturer Resources: Major refrigerant manufacturers often provide comprehensive charts on their websites. These charts are typically highly accurate and include detailed information about saturation pressures, temperatures, and other critical data. Trade publications and online forums dedicated to HVAC/R technicians also frequently share links to useful charts.
Verification is Key: When downloading charts, always verify the source’s credibility to ensure accuracy. Look for charts from reputable manufacturers or established industry organizations. Having a readily accessible PDF copy of an R134a chart is invaluable for quick reference during system diagnosis and repair, streamlining troubleshooting processes.
Safety Precautions When Working with R134a
Handling R134a refrigerant requires strict adherence to safety protocols. While considered less harmful than older refrigerants, it’s still a pressurized gas that can cause frostbite upon skin contact. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses and gloves, when working with R134a.

Ventilation is Crucial: Ensure adequate ventilation in the work area to prevent the buildup of refrigerant vapors, which can displace oxygen. Never vent R134a directly into the atmosphere; it’s a regulated substance. Proper recovery and recycling equipment must be used to reclaim the refrigerant according to environmental regulations.
System Pressures: Be mindful of the high pressures involved in AC systems. Before disconnecting any lines, ensure the system is properly depressurized. Avoid exposing R134a cylinders to extreme heat or physical damage. Familiarize yourself with the refrigerant’s Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for comprehensive safety information and emergency procedures.



